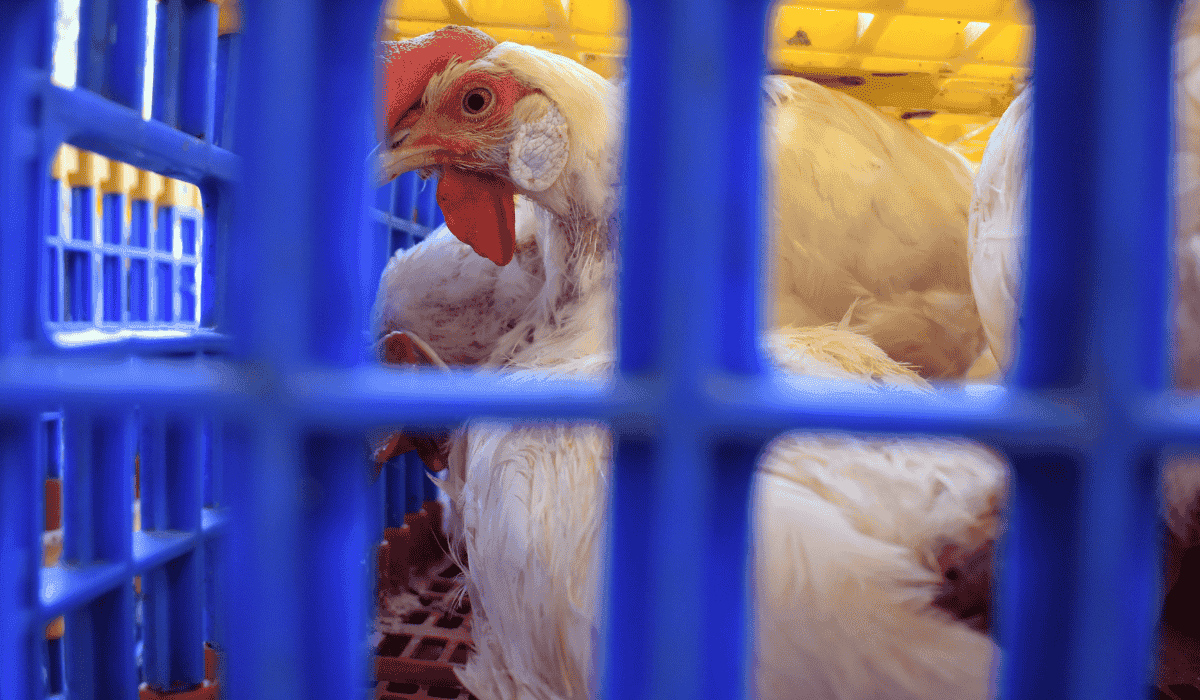
A recent bird flu outbreak in India has raised concerns, particularly in the state of Madhya Pradesh, where the virus has affected chickens and even a cat. Infected poultry has led authorities to take swift action, including shutting down poultry farms and implementing strict surveillance in affected areas. Several other states, including Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh, have also reported cases of bird flu. As the virus spreads, both health experts and local authorities emphasize the importance of preventive measures to contain the disease and protect public health. This article explores the causes of bird flu, its symptoms, and essential preventive measures to reduce the risk of infection.
Bird Flu in India: Latest Developments
The recent outbreak in Chhindwara, Madhya Pradesh, has highlighted the ongoing threat of bird flu across India. Authorities have confirmed the presence of the H5N1 strain of the virus, which has led to the closure of all poultry farms and chicken shops in the affected areas. The municipal corporation and Linga village have been placed under surveillance to monitor the spread of the disease. In addition to the chickens, a pet cat was also infected. As part of containment measures, the authorities are disposing of infected poultry and eggs safely and have imposed a ban on the sale and transport of poultry products in the affected zones.
The virus has also spread to other states, including Maharashtra, where over 7,000 poultry birds have been culled. The Animal Husbandry Department in Maharashtra has been active in controlling the outbreak, destroying thousands of eggs and culling infected birds in districts like Latur, Nanded, Nagpur, and Raigad. Similarly, Andhra Pradesh’s Godavari district has witnessed sudden deaths among chickens, and the H5N1 virus has been identified as the cause.
What is Bird Flu?
Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, is a viral infection that primarily affects birds but can occasionally spread to humans. The H5N1 strain is the most common variant that has led to human infections in the past. The virus typically spreads through direct contact with infected birds, their droppings, or contaminated surfaces. Infected animals, particularly poultry, can transmit the virus to humans, particularly those who work closely with birds, such as poultry farm workers, veterinarians, and bird handlers.
Although bird flu is primarily an animal disease, it can be fatal in humans if proper precautions are not taken. The H5N1 strain has been known to cause severe illness and, in some cases, death.
Symptoms of Bird Flu in Humans
The symptoms of bird flu in humans can initially resemble those of the common flu but often become more severe as the infection progresses. Dr. Kuldeep Kumar Grover, Head of Critical Care & Pulmonology at CK Birla Hospital, Gurugram, explains that typical symptoms of bird flu include high fever, sore throat, cough, muscle pain, and difficulty breathing. In some cases, the infection can progress to pneumonia, respiratory failure, or even death. Symptoms usually appear between 2 to 10 days after exposure to the virus.
As the infection advances, it can cause serious complications, making early diagnosis and medical intervention crucial for better outcomes. In severe cases, bird flu can lead to hospitalization or even death if not treated promptly.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Bird Flu
While bird flu poses a risk, particularly in areas where poultry farming is prevalent, there are several steps individuals can take to reduce the risk of infection. Experts emphasize the importance of hygiene and protective measures to prevent the spread of the disease.
- Avoid Direct Contact with Infected Birds
The most effective way to prevent bird flu is to avoid direct contact with infected animals. People who handle birds should take extra precautions, particularly if the birds are sick or dead. Wild birds are also known to carry the virus, and it is advisable to steer clear of areas where wild birds may be found. - Practice Good Hygiene
Frequent handwashing is critical to reducing the risk of transmission. Individuals who come into contact with birds or poultry should wash their hands thoroughly with soap and water. Surfaces that may have been contaminated with bird droppings should be disinfected regularly. - Use Protective Equipment
For individuals working closely with poultry or wild birds, it is essential to wear personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, masks, and protective clothing. This reduces the likelihood of coming into direct contact with the virus. - Cook Poultry Products Thoroughly
Cooking poultry and eggs to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) ensures that any potential viruses are killed. Consuming raw or undercooked poultry products should be avoided, especially in areas where bird flu outbreaks have been reported. - Monitor Health and Seek Medical Attention
If an individual develops flu-like symptoms after being exposed to birds or poultry, they should seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and prevent the disease from becoming severe. - Avoid Feeding Raw Poultry to Pets
Pet owners should refrain from feeding raw poultry or eggs to their pets, as this can be a source of infection. Any sick animals should be isolated and reported to authorities for further guidance.
The Role of Vaccination and Medical Treatment
While there is currently no specific vaccine for bird flu, the flu vaccine can help reduce the severity of symptoms if someone does contract the virus. However, vaccination against seasonal flu does not provide immunity against bird flu, so it is crucial to follow other preventive measures.
In the event of an infection, supportive care is the primary approach to treatment. This includes staying hydrated, resting, and using antiviral medications where necessary. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to manage complications such as pneumonia or respiratory failure.
Conclusion
The ongoing bird flu outbreaks in India serve as a reminder of the risks associated with zoonotic diseases, particularly in areas with dense poultry populations. The H5N1 strain of bird flu remains a significant concern due to its potential to cause severe illness in humans. However, by adhering to preventive measures such as avoiding contact with infected birds, maintaining good hygiene, and cooking poultry products thoroughly, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting the virus.
Authorities and health experts continue to monitor the situation closely, with surveillance efforts in affected areas and the culling of infected poultry to contain the spread. As more cases emerge, it is essential for the public to stay informed about the latest developments and follow official guidelines to stay safe.
Image source