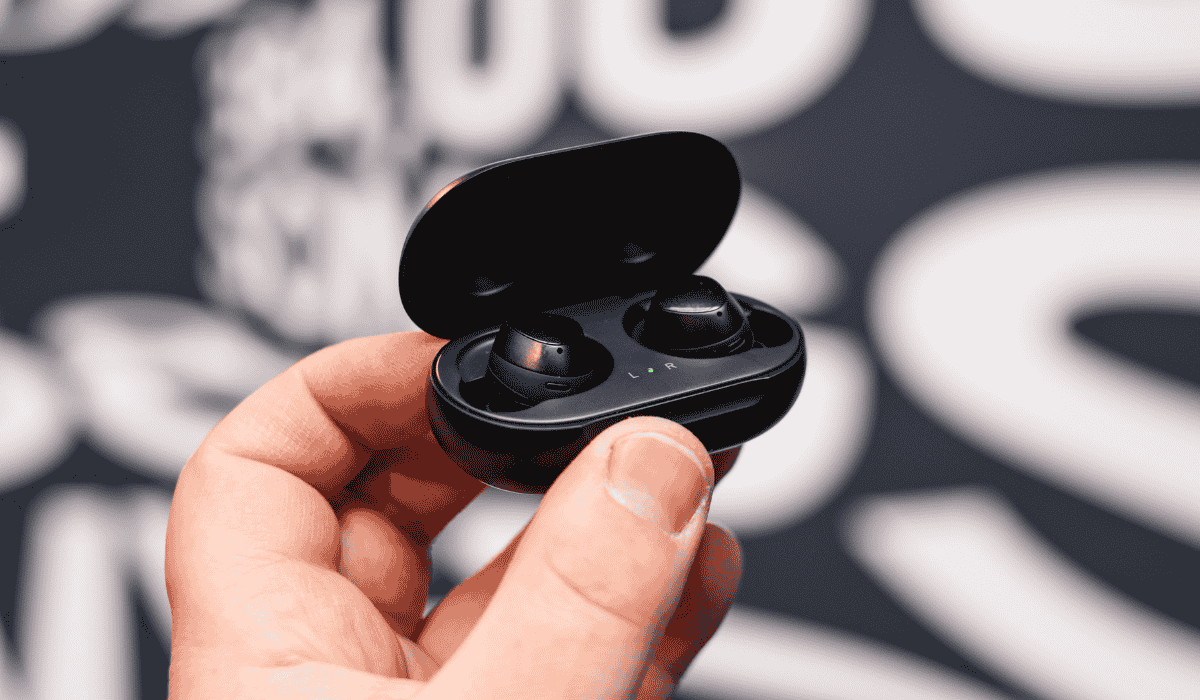
Wireless earbuds have become an essential part of our daily routines, offering the convenience of hands-free communication and high-quality sound. However, like most electronics, their battery life tends to degrade over time, often leaving users frustrated with shorter usage periods. Researchers at the University of Texas at Austin have taken a deep dive into this issue, shedding light on the reasons behind the diminishing battery performance in wireless earbuds. Their groundbreaking study, published in Advanced Materials, explores the complex interactions within these devices, focusing on how various components contribute to battery degradation.
Introduction: Understanding the Problem
The problem of battery degradation is not new, especially for portable electronic devices like wireless earbuds. Over time, users tend to notice that their earbuds no longer hold a charge as effectively as they did when new. While this issue is common in electronics, the specific causes behind it have remained somewhat of a mystery—until now. The team at UT Austin, led by Yijin Liu, an associate professor in the Cockrell School of Engineering, has set out to understand why wireless earbuds, in particular, suffer from this problem. Their research provides valuable insights into the challenges that affect battery performance, especially in devices that are exposed to varying environmental conditions.
Key Findings: Complex Interactions and Environmental Impact
The research team discovered that the decline in battery life is not solely due to the battery itself but also involves several other components within the earbuds. Wireless earbuds are compact devices that integrate a variety of parts, including the Bluetooth antenna, microphones, and circuits, all of which play a role in the device’s overall functionality. These components create a microenvironment within the earbuds, leading to complex interactions that affect battery performance.
One of the major factors identified in the study is the temperature gradient within the device. The researchers found that the battery was exposed to different temperatures at the top and bottom, which can cause damage over time. This temperature discrepancy is primarily a result of the close proximity of heat-producing components like the Bluetooth antenna to the battery. The constant fluctuation in temperature during use and charging contributes to battery wear and tear, shortening its overall lifespan.
Furthermore, the real-world environment in which the earbuds are used can have a significant impact. Extreme temperature variations, exposure to air quality changes, and unpredictable conditions all contribute to battery degradation. Although batteries are often designed to withstand harsh conditions, they are not immune to the cumulative effects of everyday use in varying environments.
The Role of User Behavior
Another key aspect of the research focuses on how individual user behavior affects battery life. According to Guannan Qian, the first author of the study, how users charge and use their earbuds can greatly influence battery performance. Charging habits, such as whether a user frequently overcharges or discharges the battery completely, can impact the battery’s longevity. Additionally, how often the earbuds are exposed to extreme temperatures—such as leaving them in a hot car or using them in cold weather—also plays a role.
The study highlights that user-specific factors, such as usage patterns, charging habits, and environmental conditions, should be considered when assessing battery performance. This personalized approach to battery behavior emphasizes the importance of understanding how these devices interact with their surroundings and how they are used.
Advanced Imaging Techniques to Uncover Hidden Dynamics
To investigate the intricacies of battery degradation, the UT Austin team employed cutting-edge imaging technologies. The researchers worked in collaboration with the university’s Fire Research Group and mechanical engineer Ofodike Ezekoye, who provided infrared imaging technology. This was paired with advanced X-ray technology to study the internal structure and behavior of the earbuds’ batteries.
The team also collaborated with several prestigious national and international institutions, including SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource, Brookhaven National Laboratory’s National Synchrotron Light Source II, Argonne National Laboratory’s Advanced Photon Source, and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in France. These facilities provided access to world-class synchrotron imaging tools, which allowed the researchers to observe the battery dynamics under real-world conditions, as opposed to the pristine or extreme conditions typically studied in laboratory settings.
X-ray imaging, in particular, offered valuable insights into how the battery’s internal structure changes over time, providing a clearer understanding of the wear and tear process that occurs as the battery ages. This research could help inform future improvements in battery design and manufacturing, making batteries more resilient to real-world conditions.
Future Research and Implications for Other Devices
While the focus of the research was on wireless earbuds, the findings could have broader implications for other battery-powered devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. The research team aims to extend their studies to larger battery cells used in these devices, exploring how similar factors affect the longevity and performance of batteries in different contexts.
Understanding the dynamics of battery degradation in real-world conditions is crucial for advancing battery technology. Liu and his team plan to continue their investigation into battery performance, with the hope of developing strategies to mitigate the damaging effects of environmental factors and improve the overall lifespan of batteries in consumer electronics.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for Battery Research
The work of the research team at the University of Texas at Austin offers valuable insights into the complex issue of battery degradation in wireless earbuds. By considering the interactions between various components within the earbuds and the effects of environmental factors, the team has illuminated key areas where improvements can be made. As the team continues their research, the findings could lead to better battery designs that are more resilient to everyday wear and tear, ultimately enhancing the user experience for a wide range of electronic devices.
Image Source